Business Service
1. Description
This service type is a regular angular service type that should implements a set of methods that are needed by the framework in order to enable advanced crud operations such as updating an entity or deleting a composite OneToMany relationship, as well as business logics.
This service type is mainly used for managing an entity as a business object.
Managing averos entities involves updating, deleting, creating, searching, or performing custom business actions on the managed entity and on its children in the context of their relationship types.
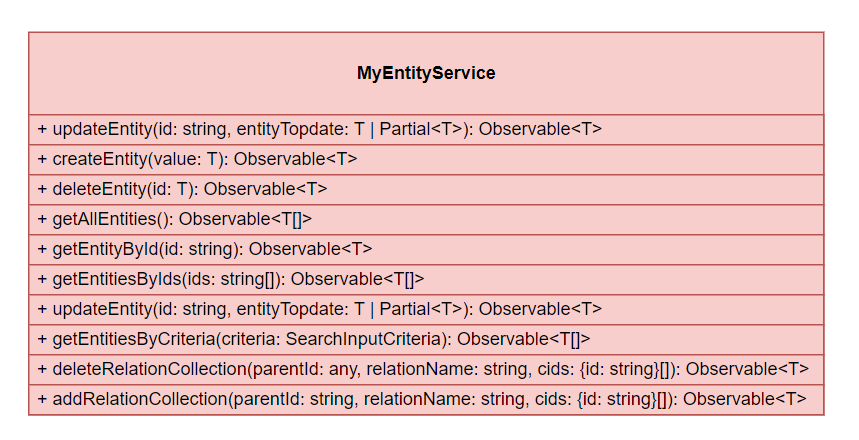
2. Business Service Class Diagram
Below is the Averos Business Service class diagram showcasing all the relevant methods that should be implemented complying with averos service guidelines.
🔖 Note that
averos-serviceworkflow, described below, will create the relevant averos service methods for you.
3. Workflow Command: averos-service
Description
Adding an averos business service could be achieved either manually or by means of the dedicated workflow command averos-service.
🔖 We recommend using
averos-servicecommand while creating business services so that the required guidelines aspects, including all required service methods, could be automatically met.
Command Usage
Below is the full detailed workflow command line:
ng g @wiforge/averos:averos-service --name=MyEntityService --ename=MyEntityName
Input Parameters
- name: Mandatory parameter. Defines the name of the service to create
- ename: Mandatory parameter. Defines the name of the entity managed by the newly created service. This entity should be created beforehand using the command
ng g @wiforge/averos:averos-entity.
🙋♂️ Please refer to averos entity section for further details about how averos framework handles business entities.
Output
The command will result in the creation of an angular service along with all the required business methods described above.
Below is a typical typescript implementation of an averos business service called MyEntityService that is managing an entity called MyEntity:
export class MyEntityService {
public static readonly SERVICE_NAME = "MyEntityService";
get apiURL(): string {
return this.environmentConfiguratorService.getApiRoute(MyEntityService.SERVICE_NAME);
}
updateEntity(id: any, entityTopdate: any | Partial<any>): Observable<any> {}
createEntity(value: any): Observable<any> {}
deleteEntity(id: any): Observable<any> {}
getAllEntities(): Observable<ToDoTask[]> {}
getEntityById(id: string): Observable<any> {}
getEntitiesByIds(ids: string[]): Observable<any> {}
getEntitiesByCriteria(criteria: SearchInputCriteria): Observable<any>{}
deleteRelationCollection(parentId: any, relationName: string, cids: {id: string}[]): Observable<any> {}
addRelationCollection(parentId: any, relationName: string, cids: {id: string}[]): Observable<any> {}
}
🙋♂️ If you intend to manually implement averos services, it is recommended that you keep the default method names and signatures in order to stay in line with the framework specifications and not to break the framework capabilities.
4. Service Configuration
Averos Services are bound to backend apis using a specific configuration types, ServiceConfiguration and GatewayConfiguration.
These configurations defines a mapping between averos service and it’s related api by binding the api location characteristics -including the server location, the communication port and protocol along with the target URI- to its target averos service attributes.
🙋♂️ Please refer to service configuration section for further details.